Describe the Four Levels of Protein Structure
Protein data bank or PDB can reveal if certain pathological condition is due to defective protein if that is the case then therapeutic effort might include correcting that defective. Related to this.

Major Differences Com Biochemistry Biochemistry Notes Protein Biology
The four levels of protein are.
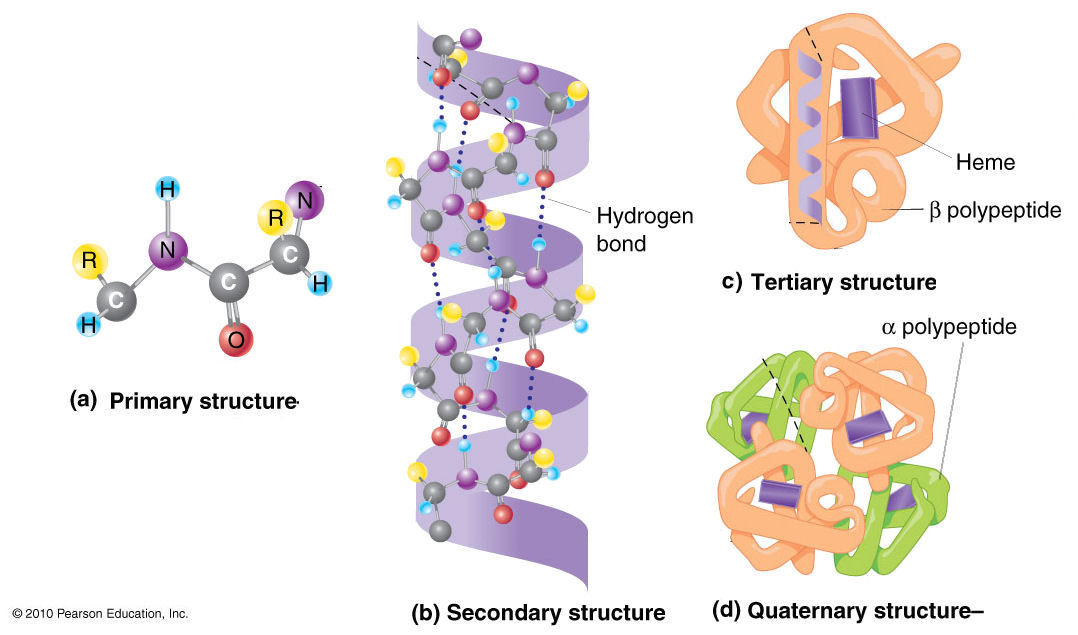
. They can also be called alpha-globins and beta-globins. Protein has multiple sub units such as hemoglobin has four sub units. There are basically 20 amino acids in a protein.
Detail the four levels of protein structure Describe the three components of a from BIOL MISC at Dixie State University. The Primary structure is the basic sequence of amino acids that form a polypeptide chain. It refers to a linear chain of amino acids connected to each other by peptide bonds.
The specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain. Local folding patterns alpha helix beta sheet etc Tertiary Structure. Name the four levels of protein structure describe the structural characteristics at each level and name the types of bonds or other forces involved at each level.
The four levels of protein structure are primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. The amino acids are connected by peptide bonds. B Describe the 4 levels of structure that proteins have.
Proteins are polymers of amino acids formed by long chains of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. Name the four levels of protein structure describe the structural characteristics at each level and name the types of bonds or other forces involved at each level. Proteins have four levels of organization Primary Structure.
There are four levels of protein structure. The sequence of amino acids Secondary Structure. Secondary structure refers to stable structural patterns of the peptide chains.
Shape formed by 2 or more polypeptide chains xraybmcuuse. Terms in this set 4 Primary Structure. Hydrogen bonds between polar amino acids ionic bonds covalent bonds between sulphur containing amino acids hydrophobic interactions between non-polar amino acids.
The Four Levels of Protein Structure. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. 1 Primary Structure 2 Secondary Structure 3 Tertiary Structure 4 Quaternary Structure The primary structure is just the amino acids bonded to each other in a.
Answer 1 of 9. Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Pleated Sheets - Hydrophobic R Group Peptide Bonds- Alpha Helix - Order of Amino Acids - Salt Bridges - Multiple Protein Chains - C Identify the R groups as being polar or nonpolar. The regular local patterns of coils or folds of a polypeptide chain.
Overall shape of a single polypeptide chain Quaternary Structure. Protein is understood as having four levels of three-dimensional structure. What type of bonds and interactions do we see in each level.
Remember each level builds upon the next to create a fully functional protein or protein cluster. The four levels of protein structures are. Also learn the structure of hemoglobin and the result of the change from its structure.
Four levels of Protein Structure. Question Describe the four levels of protein structure 1o. The four levels of protein structure are the.
This refers to various conformations that an. Understand the four structures of protein as primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. Secondary structure describes the.
Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structures. A The primary structure is the succession of amino acid residues usually abbreviated by the 1- or 3-letter codes. The primary structure of polypeptide is its amino acid sequence.
Describe the structure of proteins. 3 Dimensional structure of protein such as globular proteins. B The secondary structure is the 3-D arrangement of the right-handed alpha helix shown here or alternative structures such as a beta-pleated sheet.
Thanks for the A2A. Give the name of the fourth protein structure and what makes it. These bonds are formed by condensation reactions which allow two single amino acid molecules to join together forming a dipeptide molecule and water.
C The tertiary structure is the 3-D folding of the alpha helix show as a. The amino acid sequence in the peptide chains of the protein and the bonding between them -like peptide hydrogen sulphide describe the primary structure. Of the four globins that make up hemoglobin two are identical and called alpha chains and the other two are called beta chains and are also identical.
Alpha helix and beta pleated sheet. It is helpful to understand the nature and function of each level of protein structure in order to fully understand how a protein works. Orders of protein structure.
Protein Structure Introduction To Chemistry

Four Levels Of Protein Structure

Learn About The 4 Different Types Of Protein Structure Protein Biology Biochemistry Teaching Biology
Comments
Post a Comment